Coba
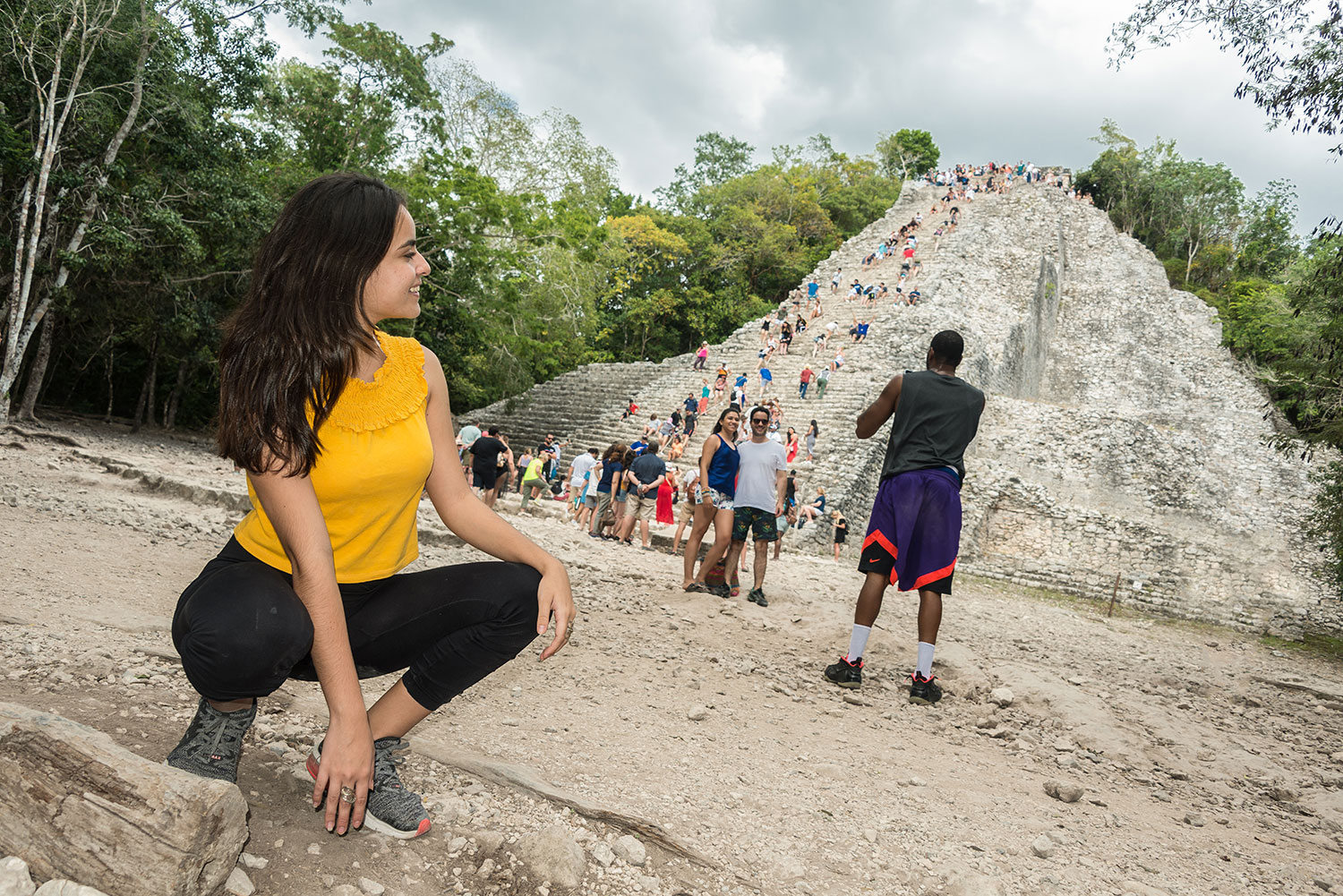
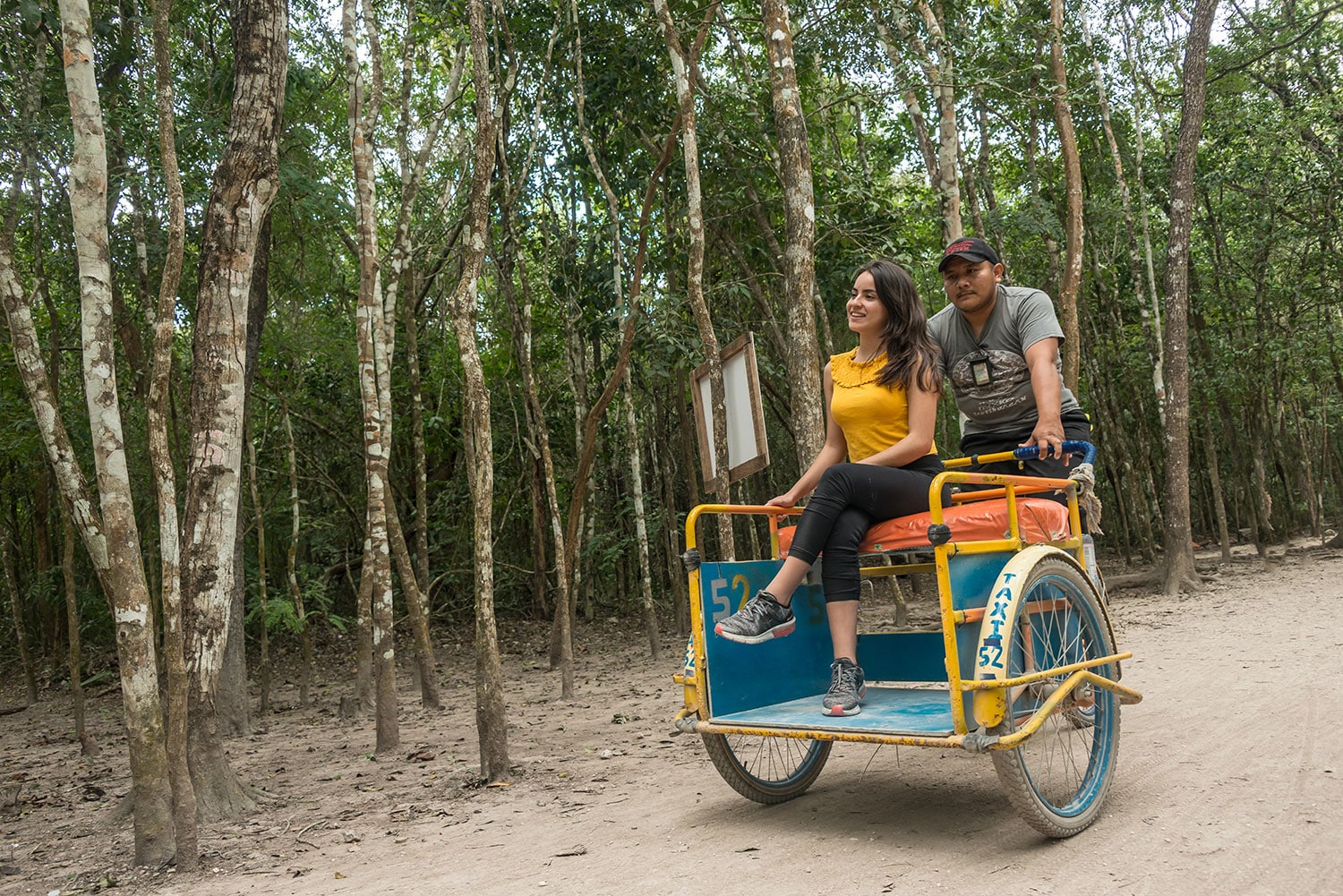
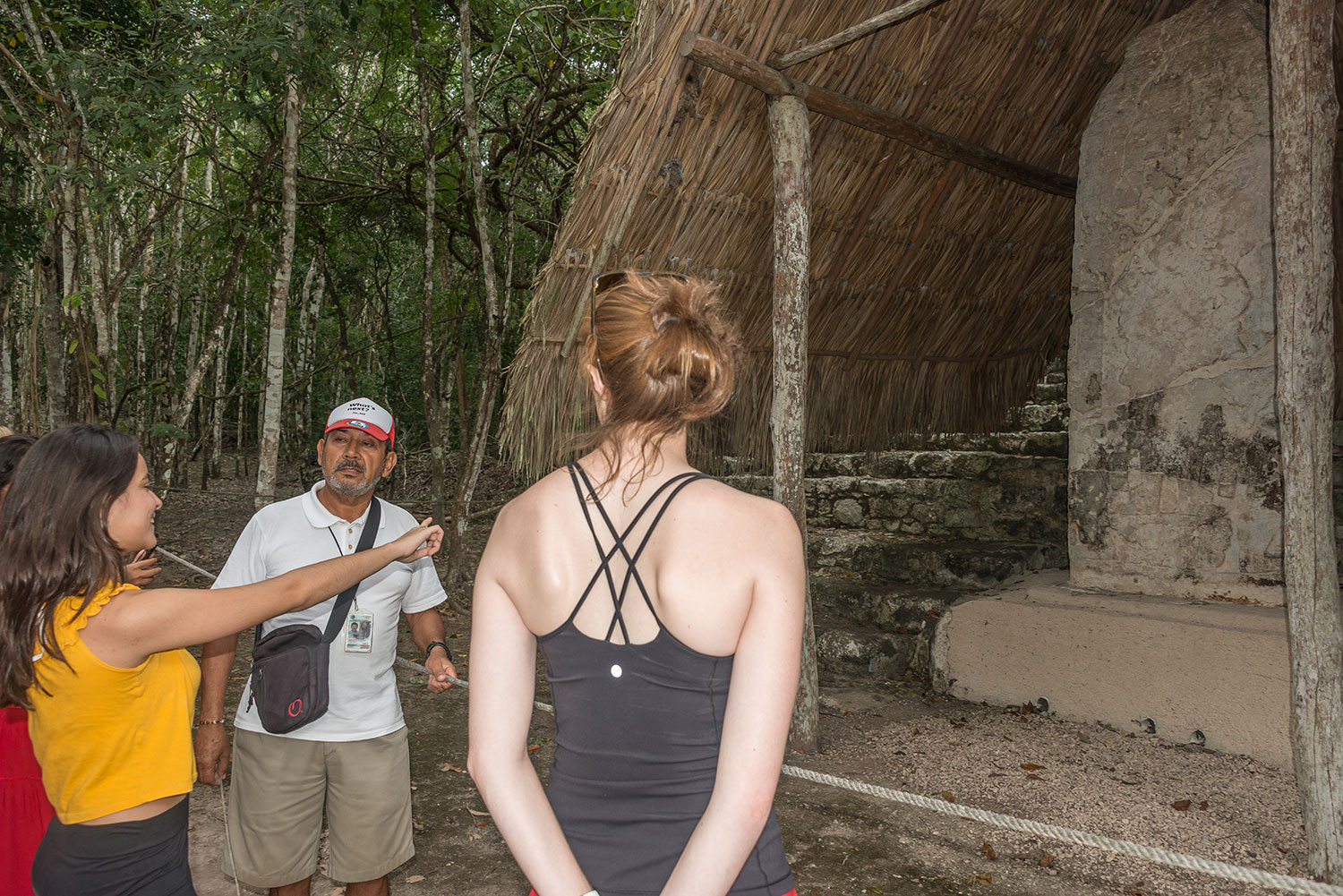
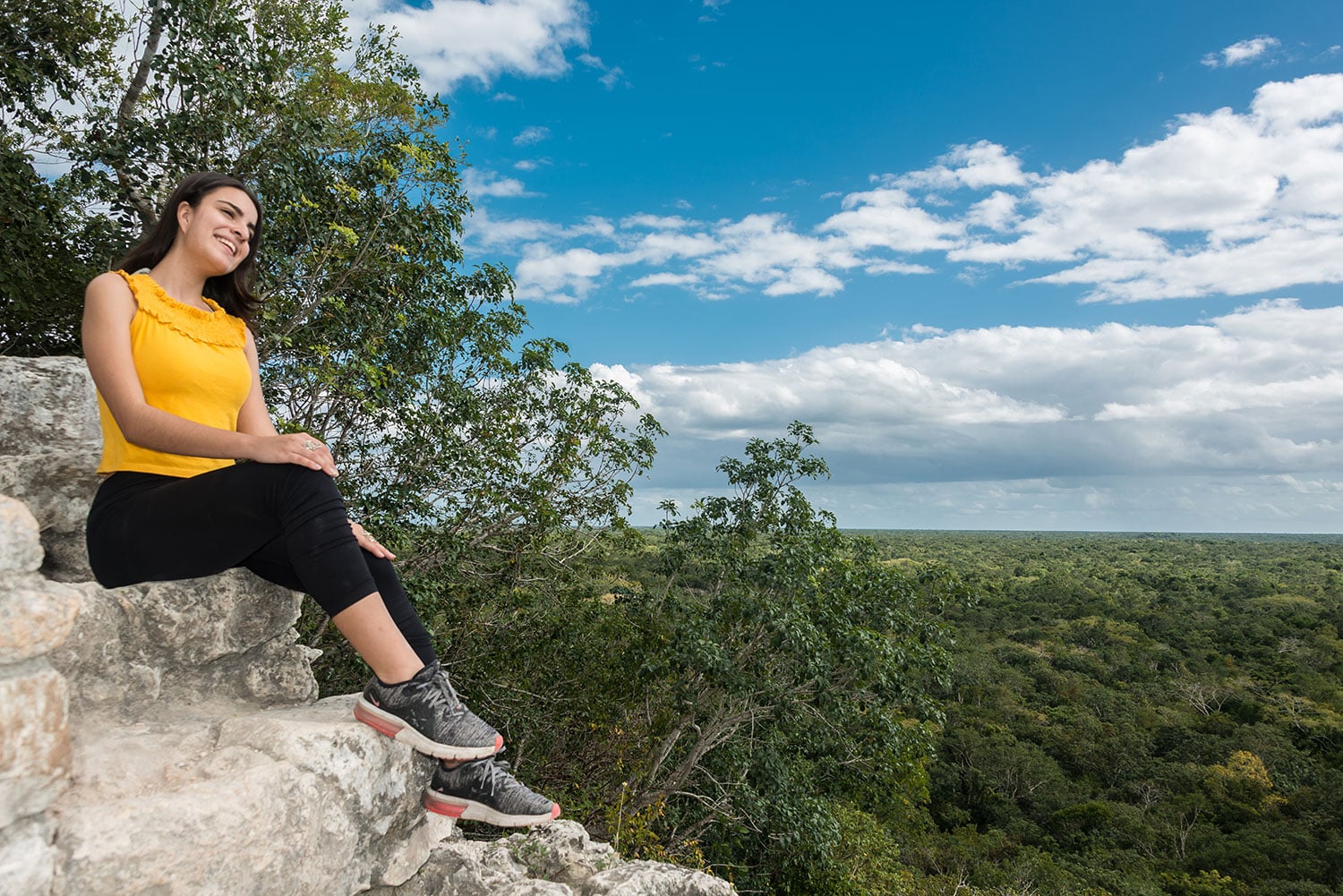
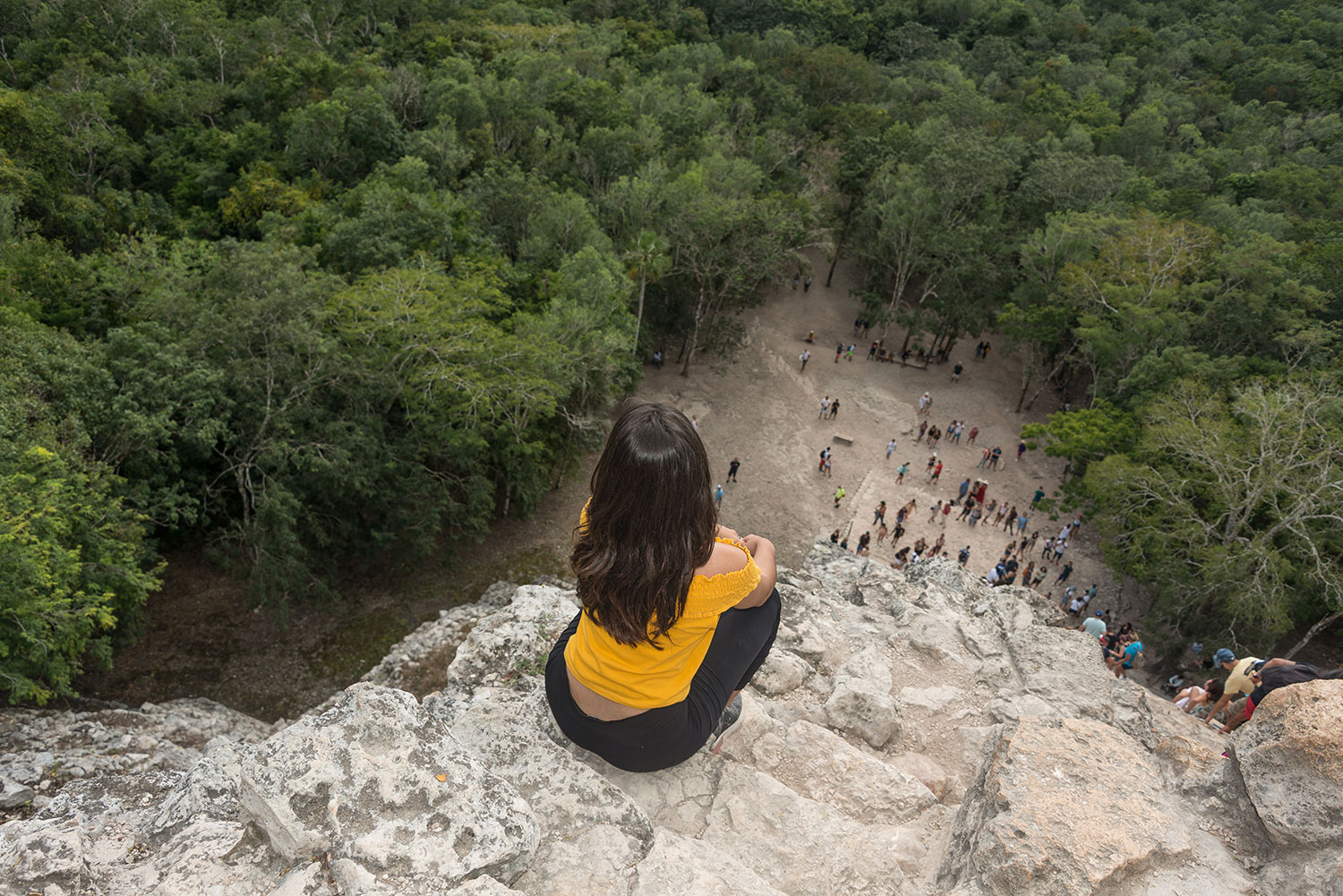
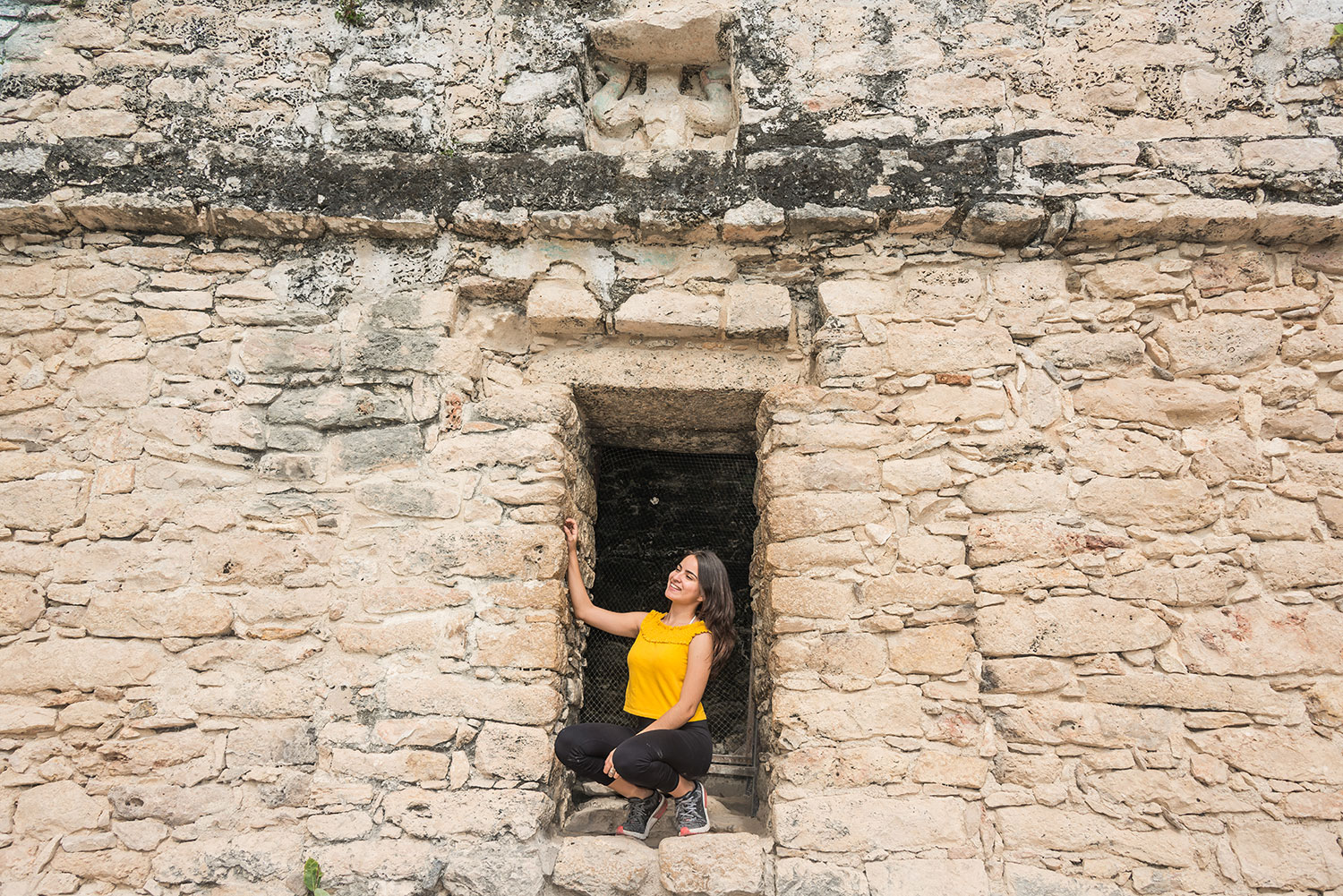
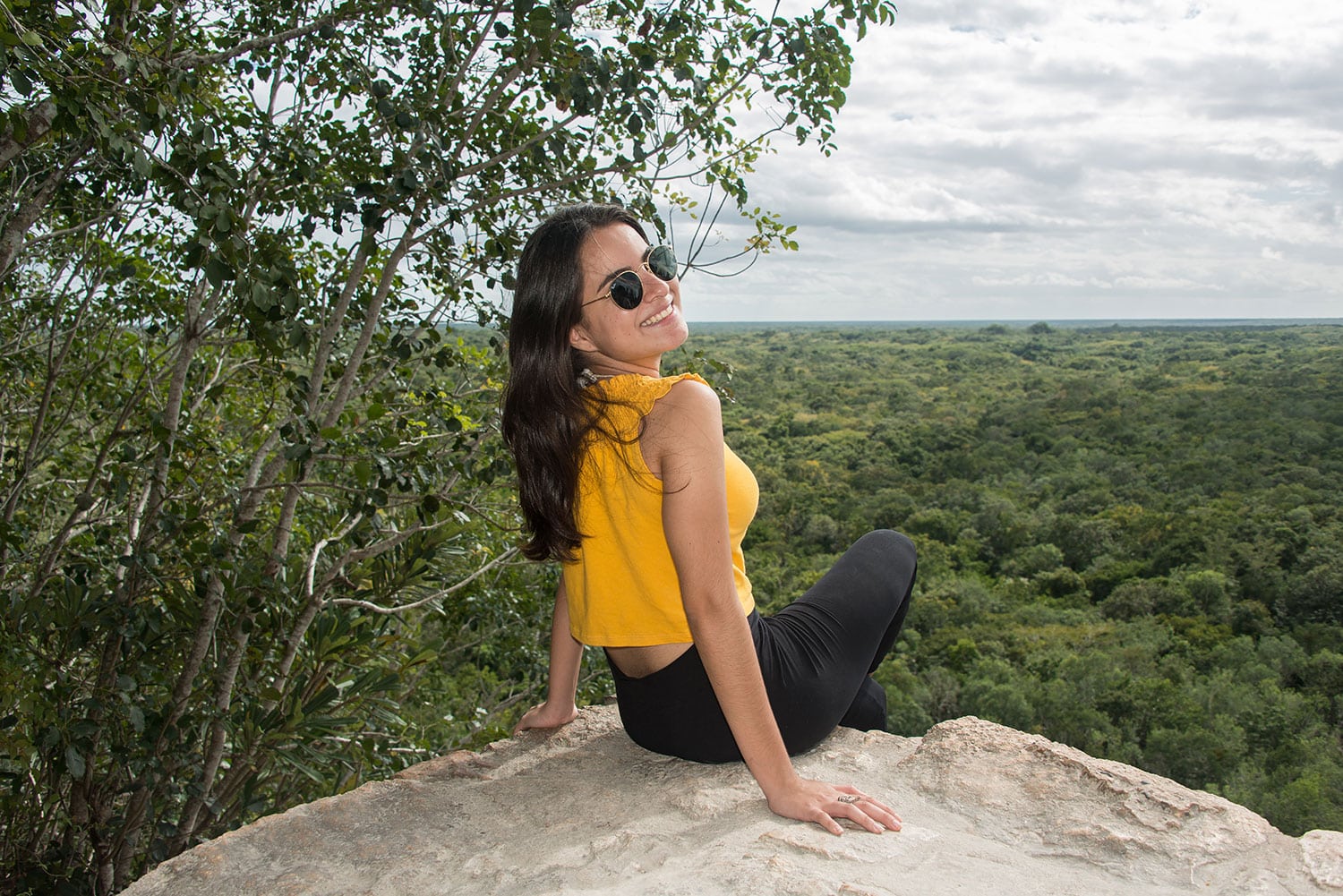
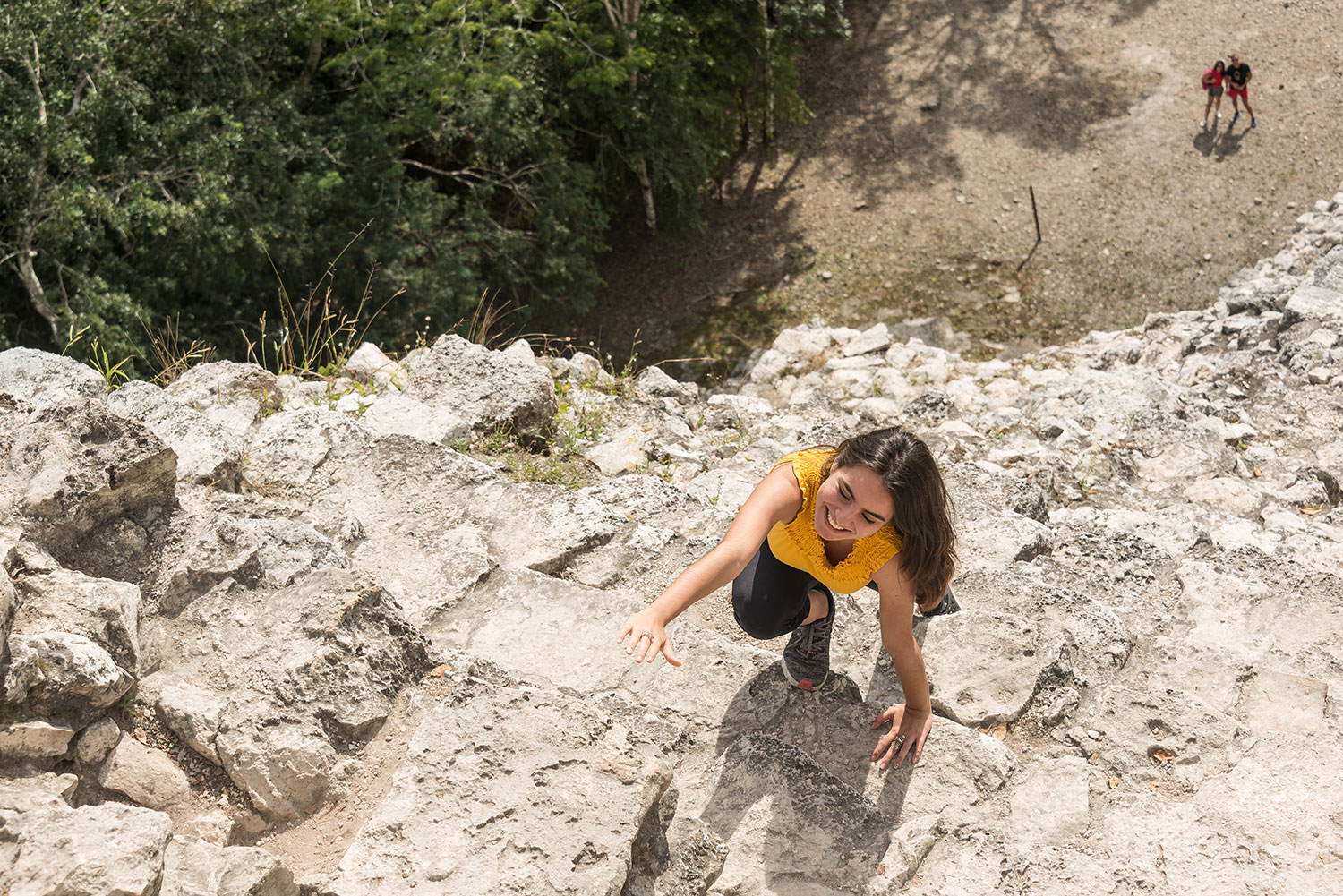
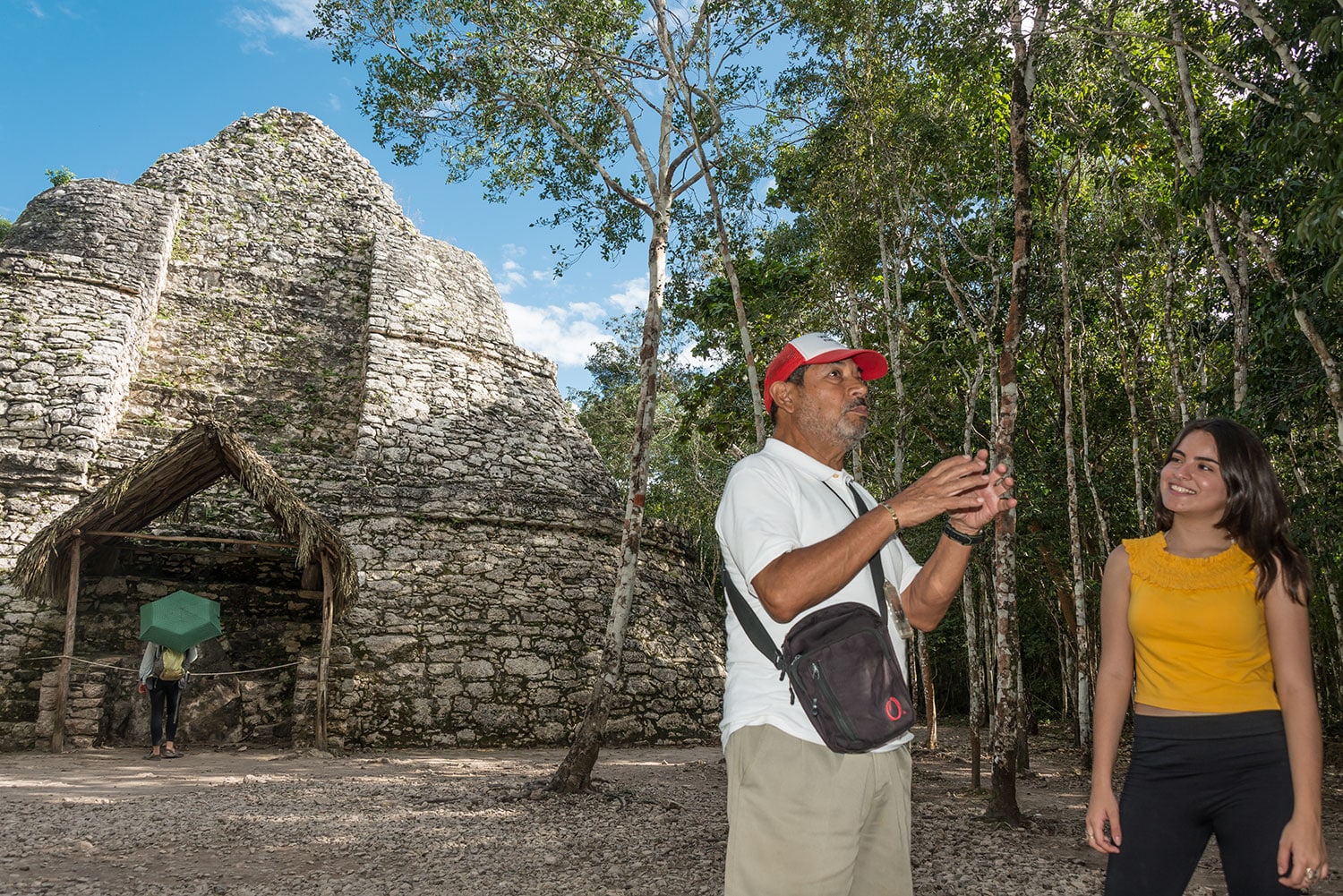
Coba (Spanish: Cobá) is an ancient Mayan city on the Yucatán Peninsula, located in the Mexican state of Quintana Roo. The site is the nexus of the largest network of stone causeways of the ancient Mayan world, and it contains many engraved and sculpted stelae that document ceremonial life and important events of the Late Classic Period (AD 600–900) of Mesoamerican civilization. The adjacent modern village bearing the same name, reported a population of 1,278 inhabitants in the 2010 Mexican federal census.
After 600 AD, the emergence of powerful city states of the Puuc culture and the emergence of Chichén Itzá altered the political spectrum in the Yucatán peninsula and began eroding the dominance of Coba. Beginning around 900 or 1000 AD, Coba must have begun a lengthy power struggle with Chichén Itzá, with the latter dominating at the end as it gained control of key cities such as Yaxuná. After 1000 AD, Coba lost much of its political weight among city states, although it maintained some symbolic and religious importance. This allowed it to maintain or recover some status, which is evidenced by the new buildings dating to the time 1200-1500 AD, now built in the typical Eastern coastal style. However, power centers and trading routes had moved to the coast, forcing cities like Coba into a secondary status, although somewhat more successful than its more ephemeral enemy Chichén Itzá. Coba was abandoned at the time the Spanish conquered the peninsula around 1550.